- The US Dollar stabilizes on Friday after a volatile week.
- Jerome Powell responded bluntly to markets and reporters on his future as Fed Chairman.
- The US Dollar index steadies in the 104-region, looking for a fresh direction.
The US Dollar (USD) stablizes around the mid-104.00 region on Friday after founding support as investors digest the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) decision to lower its monetary policy rate by 25 basis points to the 4.50%-4.75% range on Thursday. The rate cut event completely faded to the background, with reports eager to ask if Fed Chairman Jerome Powell needs to fear for his job now that President-elect Donald Trump will come to the White House in January. Powell was quite blunt and direct in saying that he will not resign and cannot be fired, underlining that the Fed is an independent body from politics in the US.
The US economic calendar sees the release of the University of Michigan’s preliminary November report on Friday. As always, a good guide and leading indicator of how consumer sentiment in the US is holding up. The inflation expectation of US consumers in the report will be a key factor after several head economists and analysts have predicted inflation will be one of the major concerns for the Trump presidency.
Daily digest market movers: Did it even matter?
- The Federal Reserve decided on Thursday to lower its monetary policy rate by 25 basis points to the 4.50%-4.75% range after the Bank of England (BoE) made the same move towards 4.75% earlier that day.
- During the press conference after the meeting, Fed Chairman Powell was asked about possible resignations or threats to his job under President-elect Trump. Powell reiterated that the Fed is an independent institute that does not follow politics and only looks at US data and its mandates. The Fed Chairman even got annoyed at one point with the question and simply said “No!” to the question, Reuters reports.
- At 15:00 GMT, the University of Michigan will release its preliminary reading for November. Consumer Sentiment is expected to tick up to 71 from 70.5 in the previous month. Inflation expectations, which were at 3% in October, have no consensus view.
- At 16:00 GMT, Federal Reserve Governor Michelle Bowman participates in a conversation about banking at a symposium organized by the University of Mississippi School of Business.
- European equities have a clear off-day with losses near 1% intraday. US futures are looking bleak as well ahead of the US opening bell.
- The CME FedWatch Tool is pricing in another 25 basis points (bps) rate cut by the Fed at the December 18 meeting by 71.3%. A smaller 28.7% chance is for rates to remain unchanged.
- The US 10-year benchmark rate trades at 4.29%, tumbling lower from this week’s high at 4.47%.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Powell is here to stay
The US Dollar Index (DXY) eased on Thursday after its steep move higher earlier in the week. That move came on the back of comments from Fed Chairman Jerome Powell that he is here to stay and will stay even when President-elect Donald Trump takes office. This reassures markets that stability will be present on the monetary policy front, and logical action will be taken to ensure the US economy does not overheat or head into hyperinflation.
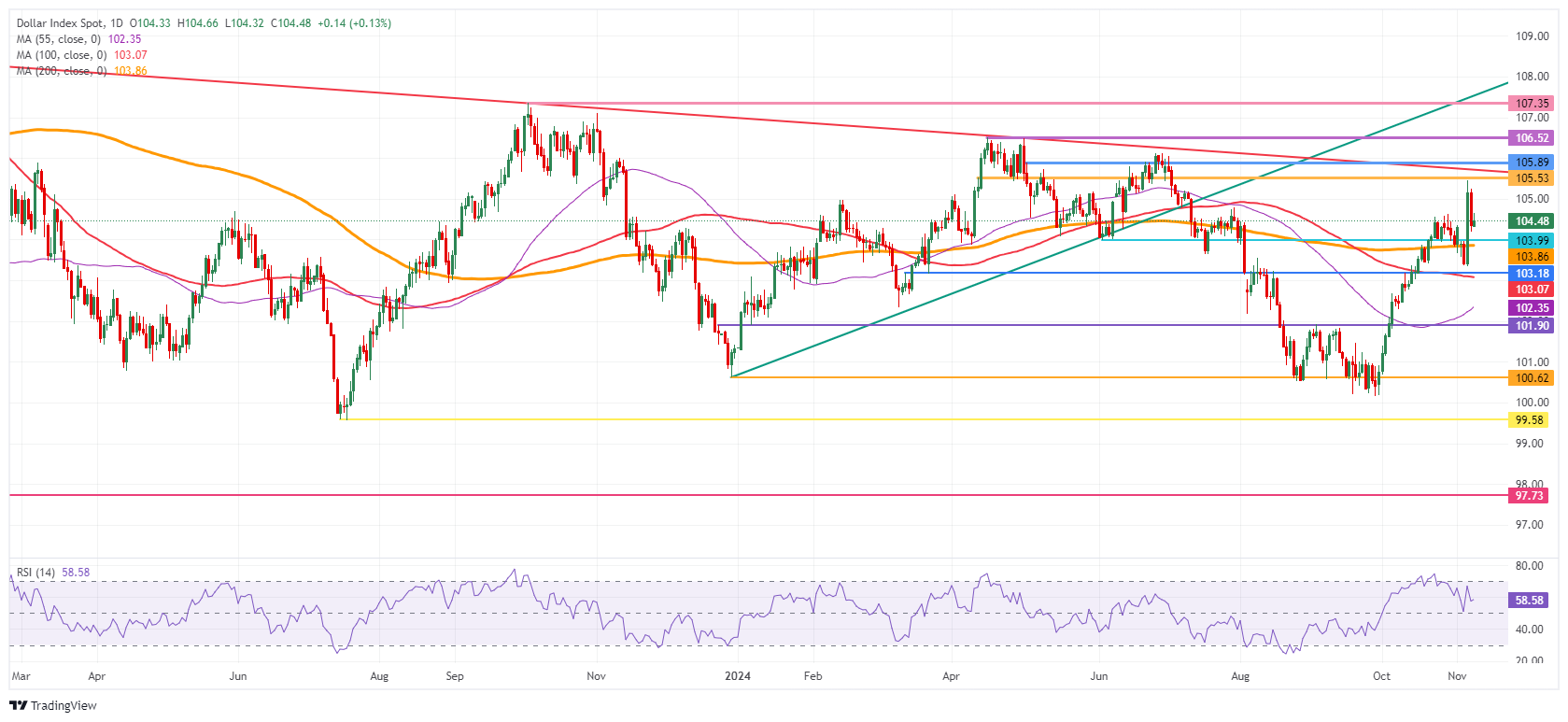
The first level to watch out for on the upside is 105.53 (April 11 high), a very firm cap resistance, with 105.89 (May 2 high) just above. Once that level is broken, 106.52, the high of April and a double top, will be the last level standing before starting to talk about 107.00.
Last week’s peak at 104.63 did not do a great job in offering some support for the fade on Thursday. On the downside, the round level of 104.00 and the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 103.86 should refrain from sending the DXY any lower.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.